

- #Human body fluid compartments series
- #Human body fluid compartments download
- #Human body fluid compartments free
Water passes through this membrane freely, but minute and big molecular weight particles do not. A cell membrane separates the intracellular compartment from the interstitial space. The matrix and cells within the interstitial space are supported by fluids. The gap between the capillaries and the cells is known as the interstitial compartment. Water and small-molecular-weight particles like as electrolytes, glucose, acetate, lactate, gluconate, and bicarbonate pass effortlessly through this capillary “membrane.” Gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide can freely pass through this membrane and enter or depart the intravascular compartment by following their concentration gradient. The endothelial glycocalyx, endothelial cells, and the subendothelial cell matrix form the capillary “membrane,” which separates the capillary intravascular region from the interstitial fluid compartment. Capillaries transport fluid from the intravascular to the interstitial and intracellular compartments. Report of the Task Group on Reference Manis, admittedly, a bit much for most readers.Intravascular, interstitial, and intracellular fluid compartments are the three major bodily fluid compartments.
#Human body fluid compartments download
And then they went and did it anyway. It is available for download in its entire 500 page glory, in case you ever need to refer to it for something as granular as the fluid content of a newbortn's thymus, or the normal boron concentration of human hair (0.2-0.8 mg/100 g, by the way). Of man which are known to be important or which are likely to be significant for estimation of dose from sources of radiation within or outside the body", because "however important or desirable it may be to have a Reference Man embodying all known characteristics of man, the task of defining such a Reference Man is clearly beyond the scope of the present effort". This thing was originally intended as an instrument to help scientists calculate dose following radiation exposure, and initially "it was agreed that the Task Group would limit its attention to those characteristics It is rarely referenced (because why would you), but if you dig around you will find that most of these textbooks get their information from the extensive and fascinating Report of the Task Group on Reference Man, by Snyder et al (1974).
#Human body fluid compartments series
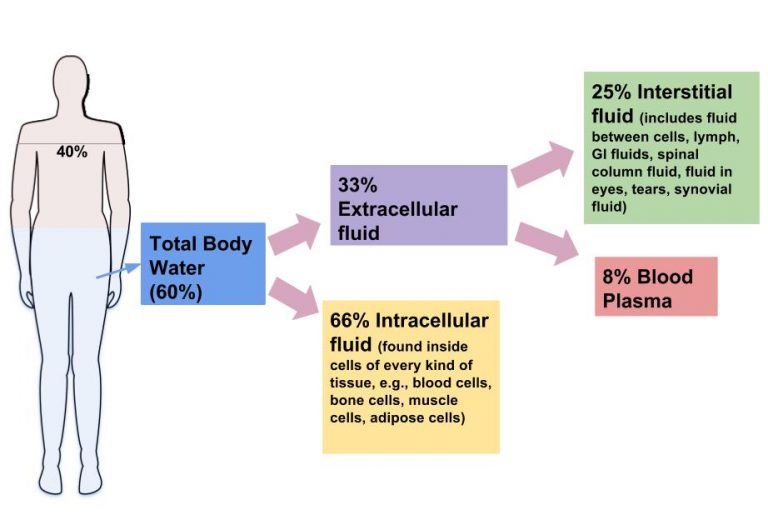
This material should seem very familiar it appears in the first chapters of almost every physiology textbook, often as a series of stacked bar graphs describing the body composition of the Ideal 70kg Person.


#Human body fluid compartments free
Intracellular Fluid = 33% ( 23.1 litres) this volume is regulated by the movement of free water.Įxtracellular Fluid = 27% (18.9 litres) this volume is regulated by the movement of sodium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
